What you need to know about heel cord injury
Exercising is a great way to remain healthy and energetic each day however; it’s helpful to know which type of exercises to perform especially if you have a sedentary lifestyle.
Advertisement
This is to allow to you to enjoy your exercise regime and prevent any injuries from occurring.
Also, individuals who already have a training schedule, may also prevent injuries by not overloading themselves with too much to perform too quickly. Adhering to a healthy training plan may prevent you from heel cord injuries.
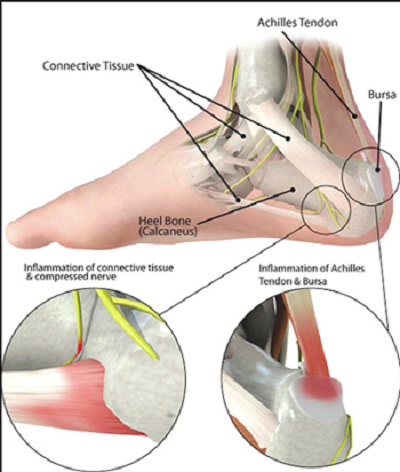
The condition results from overstretching or tearing of the heel cord/ Achilles tendon in the leg.
The tendon is a strong band that connects the muscles in your leg to your heel bone. The tendon assists in absorbing the force of body during walking, jumping, running etc and also assists in the downward movement of the foot.
Heel cord injury is a persistent condition which is accompanied by stiffness and pain at the back of the leg close to your heel. The condition results from various risk factors such as having too much tightness in the calf muscles or a sudden increase in your activities.
Some individuals acquire the condition as a result of excessive training over a prolonged period of time.
Risk factors
There are a number of risk factors linked to heel cord injury. The condition is associated with an abrupt or swift change in training schedules or intensities without allowing your muscles to gradually build up strength.
The swift change places a lot of strain on your calf muscles and in its effort to sustain the extra load, it works harder and this results in injury to your heel cord.
Excessive training is also linked with the condition. Excessive training implies performing too many activities too quickly.
This also overloads your muscles each time you train, and causes small tears in the Achilles tendon over a prolonged period of time.
And when you do not permit yourself to recover appropriately from these small injuries but you keep pushing yourself to train, eventually the tendon injury becomes very painful and places a halt on your activities.
It cannot be gainsaid that appropriate warm-up and cool down is expedient each time you exercise. This prepares your muscles to begin the exercises and also keeps them conditioned after you complete the exercises to prevent injuries.
Other risk factors include;
- Returning to normal activities after a previous foot or ankle injury
- Wearing inappropriate footwear for exercises
- Poor foot flexibility
- Exercising repeatedly on a rough or uneven ground or surface
- Excessive uphill running
- Improper training or exercise programme
- Individuals with a high arch or flat feet
- Tightness or weakness in the leg muscles
- Sudden or sharp movements that forces the calf muscles to abruptly contract places a lot of undue stress on the tendon and minimal time period to recover
- A violent strain may also cause injury to the calf muscles or the Achilles tendon.
For instance, inappropriate landing on the ground after a jump may cause an awkward foot placement on the ground resulting in injury.
- Inappropriate treatment of a previous foot or ankle injury
Symptoms
The symptoms of the condition tend to develop slowly over a period of time. Heel cord injury results in a gradual onset of pain in the heel cord which increases after you perform an activity such as walking around.
Some individuals may also feel the pain especially in the morning just above the heel bone.
After a while as the condition becomes worse, you experience pain during all the activities you perform. Rising up on your toes may also cause increase in pain. And you may also experience stiffness in your ankle joint which may be relieved by activities.
Standing or taking steps also may become difficult.
Diagnosis
The clinical history and physical examination of the affected leg, heel and ankle joint may show swelling around the ankle joint which is painful to touch.
The movement of the foot is performed in different directions to determine the level of stiffness in the ankle joint.
Before the condition is diagnosed, further investigations of the affected leg is conducted which includes X-rays, MRI or ultrasound.



