Deep vein thrombosis and diet
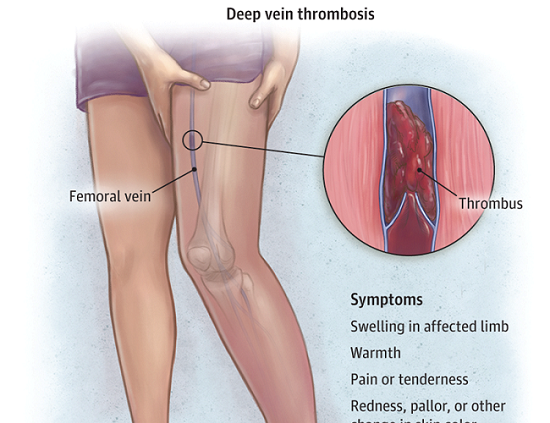
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a blood clot (thrombus) inside a deep vein in the body, often in the thigh or calf.
Advertisement
These clots occur most readily within the legs, although they can also occur within other areas of the body as well.
DVT is the result of three principal factors described by Dr Virchow in the 1860’s.
These are; reduced or stagnant blood flow in deep veins (venous stasis), injury to the blood vessel wall and an increase in the activity of those substances in the blood that are part of the normal clotting mechanism, a condition called hypercoagulability (which means a more active clotting state).
Symptoms
Many cases of DVT occur without any noticeable symptoms. The following symptoms occur in a few instances; swelling in the leg, foot and ankle; redness, warmth and pain.
If a clot forms in the arm, symptoms include swelling and pain in the arm and neck. When these symptoms develop, the sufferer should go to the hospital. This will then lead to an early detection of DVT and increased success of treatment.
Often people overlook these symptoms leading to a complicated DVT with treatment outcomes becoming unfavourable.
Watch these factors
A number of factors increase the possibility of developing DVT. These include: prolonged immobilization (such as lying in bed following surgery, sitting for long periods say one and a half hours or more which reduces circulation in legs by 50% and being on a long flight), having undergone a surgical procedure, having been subjected to major trauma, increasing age and malignancy (cancerous tumour).
The rest are heart failure, a previous bout with deep vein thrombosis, pregnancy, the use of oral contraceptives, diabetes (a disorder in which the body cannot make use of sugars and starches in a normal way; diabetes also damages blood vessels), obesity - weight puts pressure on veins, causing them to weaken, childbirth - physical strain of childbirth puts pressure on deep veins, causing them to weaken, tobacco smoking - damages blood vessels and doubles the risk of thrombosis.
Possible outcome
The danger of DVT is that the clot can become dislodged (break from its location) and travel throughout the body's veins until it gets into the lungs where obstruction takes place. The final result is a pulmonary embolism.
After treatment, one can still develop another DVT. Here, your doctor will help you take some precautions that will help prevent further clots from forming.
It is very helpful to follow a targeted diet so as to reduce one’s chances of contracting this condition by dealing with some of the risk factors such as high blood cholesterol, overweight and obesity, diabetes, among others.